Microsoft Azure Log Ingestion (om_azuremonitor)
This module forwards logs to Azure services that support the Azure Monitor Logs Ingestion API. Event data is sent in batches, reducing the latency caused by the HTTP responses, thus improving Microsoft Azure’s server performance.
Configuring a Microsoft Azure AD application
You must first create a Microsoft Azure AD application to use any Microsoft API. You will need the following details to configure the om_azuremonitor module:
-
An Application (client) ID
-
The Directory (tenant) ID
-
A client secret or a certificate and private key pair.
See Add credentials on Microsoft Docs for more information.
Register an Azure application
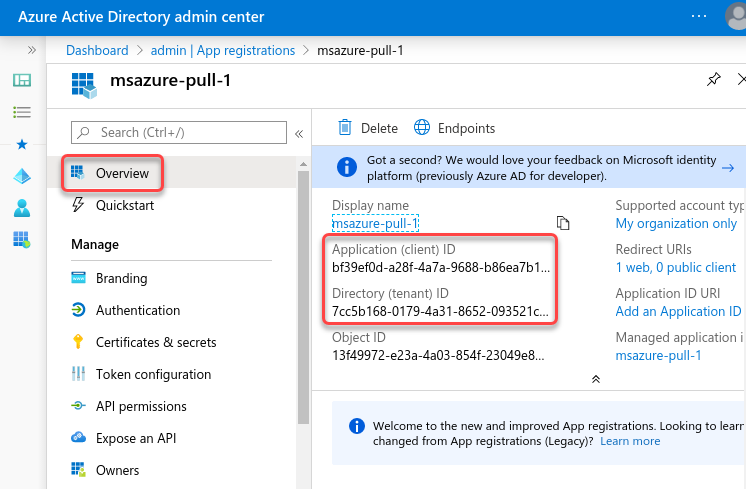
First, follow the instructions to Register an application on Microsoft Learn. Once you have created the new application, take note of the Application (client) ID and the Directory (tenant) ID from the application Overview page.
Generate an X.509 certificate
To use certificate-based authentication to authenticate with Microsoft’s APIs, you need an X.509 certificate and the private key used to generate the certificate. The following instructions guide you through creating the private key pair using OpenSSL.
-
Save the following script in a file named
gencertkey.sh#!/bin/sh openssl req -new -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -x509 -days 730 -keyout certkey.pem -out cert.pem #openssl pkcs12 -export -out cert.pfx -inkey certkey.pem -in cert.pem openssl x509 -outform der -in cert.pem -out cert.der cat cert.der |openssl dgst -binary -sha1 | openssl base64 >cert.base64thumb THUMBPRINT=`cat cert.base64thumb` echo "ThumbPrint:$THUMBPRINT" UUID=`uuidgen` CERT=`cat cert.pem | grep -v "\-\-\-\-"| tr -d '\n'` cat <<EOF "keyCredentials": [ { "customKeyIdentifier":"$THUMBPRINT", "keyId":"$UUID", "type":"AsymmetricX509Cert", "usage":"Verify", "value":"$CERT" } ], EOF -
The script depends on the
openssltoolkit and theuuidgenprogram. Install the corresponding packages if necessary.On Debian-based platforms:
# apt install openssl uuid-runtimeOn Centos/Red Hat platforms:
# yum install openssl util-linux -
Execute
gencertkey.shon the computer where NXLog is installed to generate the certificate.$ ./gencertkey.shThe output:
Generating a RSA private key ............+++++ ................................................+++++ writing new private key to 'certkey.pem' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]: State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]: Locality Name (eg, city) []: Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]: Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []: Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []: Email Address []: ThumbPrint:0nFt3fB0JP7zuSmHaRQtmsFNYqo= "keyCredentials": [ { "customKeyIdentifier":"0nFt3fB0JP7zuSmHaRQtmsFNYqo=", "keyId":"629ab88d-1059-454b-b258-4ca05b46dee4", "type":"AsymmetricX509Cert", "usage":"Verify", "value":"MIIDXTCCAkWgAwIBAgIJAP+XrnwhAxjOMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMEUxCzAJB..." } ], -------- + Take note of the `ThumbPrint` and `KeyCredentials` values. -
Go to the Microsoft Azure AD application registration page, select Manifest on the left, and click Download.
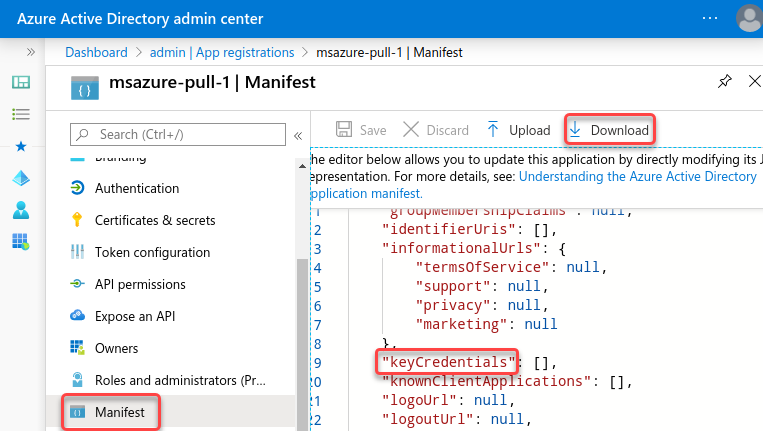
-
Edit the downloaded manifest file and replace the KeyCredentials value with the value from the previous step.
"keyCredentials": [ { "customKeyIdentifier":"0nFt3fB0JP7zuSmHaRQtmsFNYqo=", "keyId":"629ab88d-1059-454b-b258-4ca05b46dee4", "type":"AsymmetricX509Cert", "usage":"Verify", "value":"MIIDXTCCAkWgAwIBAgIJAP+XrnwhAxjOMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMEUxCzAJB..." } ], -
Save the changes and upload the manifest to Microsoft Azure.
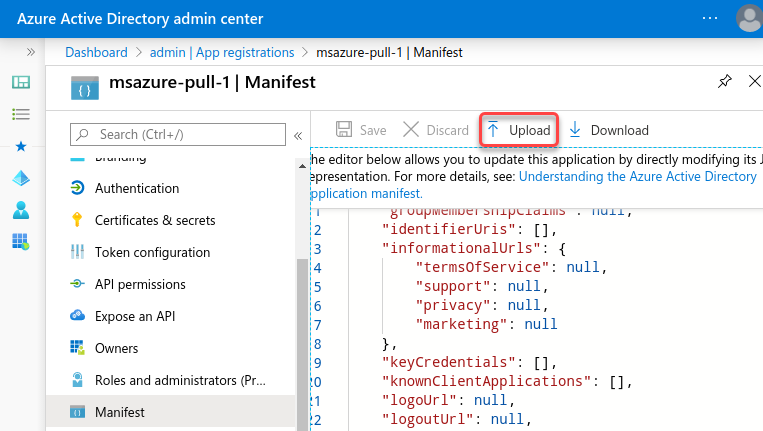
Output log format
om_azuremonitor forwards log records over HTTP(S) as JSON payload.
The JSON format depends on the value of the $raw_event field.
The module checks if the value of $raw_event is valid JSON and applies the following rules:
-
If it is valid JSON, the value is forwarded as is.
-
If it is not valid JSON, the log record is converted to JSON in the following format:
{ "raw_event": "<json_escaped_raw_event>" }
Additional metadata, including the NXLog-specific fields EventReceivedTime, SourceModuleName, and SourceModuleType, will not be included in the output unless these values have been written to the $raw_event field.
The processing required to achieve this depends on the format of the input data, but generally it means you need to:
-
Parse the log record according to the data format.
-
If the input data is already in JSON format, use parse_json() to parse
$raw_eventinto fields. -
If the input is unstructured plain text data, copy the value of
$raw_eventto a custom field.
-
-
Create and populate any additional custom fields.
-
Use to_json() to convert the fields to JSON format and update the value of
$raw_event.
See the Examples section for NXLog configuration examples of the above.
Configuration
The om_azuremonitor module accepts the following directives in addition to the common module directives. The ClientId, TenantId, ClientSecret, DcrImmutableId, TenantId, TableName and URL directives are required.
- ClientId
-
This mandatory directive specifies the Microsoft Azure App
Application (client) ID.
- TenantId
-
This mandatory directive specifies the Microsoft Azure App
Directory (tenant) ID.
- ClientSecret
-
Specifies the Microsoft Azure App client secret. This directive is mutually exclusive with the CertThumbprint and CertKeyFile directives.
- CertThumbprint
-
Specifies the thumbprint of the certificate that will be presented to the remote server during Azure Certificate Authentication. This value corresponds to the hexadecimal fingerprint string generated by
gencertkey.shwhen Generating the X.509 certificate. This directive is mutually exclusive with the Secret directive.The private key associated with the certificate must be exportable.
-
If you generate the certificate request using Windows Certificate Manager, enable the Make private key exportable option from the certificate properties.
-
If you import the certificate with the Windows Certificate Import Wizard, make sure that the Mark this key as exportable option is enabled.
-
If you migrate the certificate and associated private key from one Windows machine to another, select Yes, export the private key when exporting from the source machine.
-
- CertKeyFile
-
Specifies the path of the private key file that was used to generate the certificate specified by the CertThumbprint directive. This directive is mutually exclusive with the Secret directive.
- DcrImmutableId
-
Specifies the ID of the Data Collection Rule (DCR) to use for Azure Monitor to ingest the logs.
- URL
-
Specifies the Data Collection Endpoint (DCE) URI.
- TableName
-
The name of the table where to store the logs. You must prefix custom table names with
Custom-.
- Reconnect
-
This optional directive sets the reconnect interval in seconds. If it is set, the module attempts to reconnect in every defined second. If it is not set, the reconnect interval will start at 1 second and doubles on every attempt. If the duration of the successful connection is greater than the current reconnect interval, then the reconnect interval will be reset to 1 sec.
- AzureBatchSize
-
Maximum size of the request in bytes. The default is 1 MB.
- Connections
-
Number of allowed parallel HTTP connections. More connections mean bigger throughput. The default is 1.
- AuthURL
-
This directive specifies the URL for authenticating with the API. The default value is
https://login.microsoftonline.com.
Examples
To send data to a custom table, you must create a data collection endpoint (DCE) and a data collection rule (DCR) in Microsoft Azure. Instructions are available in the Microsoft Learn tutorial Send data to Azure Monitor Logs by using a REST API. Once you have your DCE and DCR set up, configure an om_azuremonitor instance as follows.
<Output azure_monitor>
Module om_azuremonitor
ClientId <CLIENT_ID>
TenantId <TENANT_ID>
ClientSecret <CLIENT_SECRET>
URL <DATA_COLLECTION_ENDPOINT>
DcrImmutableId <DCR_IMUTABLE_ID>
TableName Custom-<CUSTOM_TABLE_NAME>
</Output>To send data to a built-in table, you must create a data collection endpoint (DCE) and a data collection rule (DCR) in Microsoft Azure using one of the following templates:
The template automatically creates a data collection rule (DCR) to redirect logs from Custom-MyTableRawData to the desired table.
Currently, it is not possible to insert records directly into built-in tables.
See Create a data collection endpoint on Microsoft Learn for more information.
Once you have your DCE and DCR set up, configure an om_azuremonitor instance as follows. The destination table name corresponds to the table created by the template.
<Output azure_monitor>
Module om_azuremonitor
ClientId <CLIENT_ID>
TenantId <TENANT_ID>
ClientSecret <CLIENT_SECRET>
URL <DATA_COLLECTION_ENDPOINT>
DcrImmutableId <DCR_IMUTABLE_ID> # The ID of the DCR created by the template
TableName Custom-MyTableRawData
</Output>