Nagios Log Server
Nagios Log Server provides centralized management, monitoring, and analysis of logging data. It utilizes the ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana) stack. NXLog can be customized to send log data to the Nagios Log Server over TCP, UDP, and TLS/SSL protocols.
Installation and configuration of Nagios Log Server
To learn more about installation and configuration of Nagios Log Server, see the Manual Installation Instructions and Administrator Guide on the Nagios website.
By default, Nagios Log Server does not require any post-installation configuration which means logs can be received from NXLog right away.
NXLog configuration
NXLog can be configured to send the logs it collects to Nagios Log Server.
To see the IP address and ports of the Nagios Log Server instance, open the Configure page and find the Configuration Editor section.

These address and ports will be used in the examples below.
The configuration below reads systemd messages using the
im_systemd module and selects only those entries which contain
the sshd character combination.
The selected messages are processed with the xm_kvp module and
converted to JSON using the xm_json module.
Sending over TCP is carried out using the om_tcp module.
<Extension kvp>
Module xm_kvp
KVDelimiter =
KVPDelimiter " "
</Extension>
<Extension json>
Module xm_json
</Extension>
<Input systemd>
Module im_systemd
ReadFromLast TRUE
Exec if not ($raw_event =~ /sshd/) drop();
</Input>
<Output out>
Module om_tcp
Host 192.168.31.179
Port 3515
<Exec>
kvp->parse_kvp();
to_json();
</Exec>
</Output>Below is the event sample of a log message which is sent over TCP.
{
"Severity": "info",
"SeverityValue": 6,
"Facility": "syslog",
"FacilityValue": 4,
"Message": "Accepted password for administrator from 192.168.31.179 port 46534 ssh2",
"SourceName": "sshd",
"ProcessID": 3168,
"User": "root",
"Group": "root",
"ProcessName": "sshd",
"ProcessExecutable": "/usr/sbin/sshd",
"ProcessCmdLine": "sshd: administrator [priv]",
"Capabilities": "3fffffffff",
"SystemdCGroup": "/system.slice/ssh.service",
"SystemdUnit": "ssh.service",
"SystemdSlice": "system.slice",
"SelinuxContext": "unconfined\n",
"EventTime": "2020-03-25 18:59:53",
"BootID": "1eb2f28ae8064c7a954e2420be54a7f2",
"MachineID": "0823d4a95f464afeb0021a7e75a1b693",
"SysInvID": "984c8a16fd20462a9ac8c0682081979c",
"Hostname": "ubuntu",
"Transport": "syslog",
"EventReceivedTime": "2020-03-25T18:59:53.565177+00:00",
"SourceModuleName": "systemd",
"SourceModuleType": "im_systemd"
}The configuration below reads Windows Event Log entries and selects only those
entries which contain IDs 4624 and 4625 using
the im_msvistalog module.
The collected logs are then converted to JSON using the xm_json
module after the Message field is deleted from the entry.
Sending over UDP is carried out using the om_udp module.
<Extension json>
Module xm_json
</Extension>
<Input in_eventlog>
Module im_msvistalog
<QueryXML>
<QueryList>
<Query Id="0">
<Select Path="Security">
*[System[Level=0 and (EventID=4624 or EventID=4625)]]</Select>
</Query>
</QueryList>
</QueryXML>
<Exec>
delete($Message);
json->to_json();
</Exec>
</Input>
<Output out>
Module om_udp
Host 192.168.31.179
Port 5544
Exec to_json();
</Output>Below is the event sample of a log message which is sent over UDP.
{
"EventTime": "2020-03-22T13:48:55.455545-07:00",
"Hostname": "WIN-IVR26CIVSF6",
"Keywords": "9232379236109516800",
"EventType": "AUDIT_SUCCESS",
"SeverityValue": 2,
"Severity": "INFO",
"EventID": 4624,
"SourceName": "Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing",
"ProviderGuid": "{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}",
"Version": 2,
"TaskValue": 12544,
"OpcodeValue": 0,
"RecordNumber": 15033,
"ActivityID": "{CFEB8893-00D2-0000-E289-EBCFD200D601}",
"ExecutionProcessID": 532,
"ExecutionThreadID": 572,
"Channel": "Security",
"Category": "Logon",
"Opcode": "Info",
"SubjectUserSid": "S-1-5-18",
"SubjectUserName": "WIN-IVR26CIVSF6$",
"SubjectDomainName": "WORKGROUP",
"SubjectLogonId": "0x3e7",
"TargetUserSid": "S-1-5-90-0-6",
"TargetUserName": "DWM-6",
"TargetDomainName": "Window Manager",
"TargetLogonId": "0x1c8f13",
"LogonType": "2",
"LogonProcessName": "Advapi ",
"AuthenticationPackageName": "Negotiate",
"WorkstationName": "-",
"LogonGuid": "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000}",
"TransmittedServices": "-",
"LmPackageName": "-",
"KeyLength": "0",
"ProcessId": "0x848",
"ProcessName": "C:\\Windows\\System32\\winlogon.exe",
"IpAddress": "-",
"IpPort": "-",
"ImpersonationLevel": "%%1833",
"RestrictedAdminMode": "-",
"TargetOutboundUserName": "-",
"TargetOutboundDomainName": "-",
"VirtualAccount": "%%1842",
"TargetLinkedLogonId": "0x1c8f24",
"ElevatedToken": "%%1842",
"EventReceivedTime": "2020-03-22T13:48:56.870657-07:00",
"SourceModuleName": "in",
"SourceModuleType": "im_msvistalog"
}Configuration of NXLog for sending logs over SSL/TLS is already described in the Sending NXLogs With SSL/TLS section on the Nagios website.
To read more about encrypted transfer of data, see the Encrypted log transfer and TLS/SSL (om_ssl) chapters in the NXLog documentation.
Other examples of sending log data using NXLog from the Nagios website:
Verifying data collection
To verify successful collection by the Nagios Log Server, open the Home page and add the relevant log source.
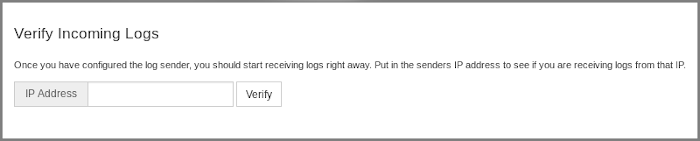
On the log source page, find the Verify Incoming Logs section, type in the IP address of the NXLog server and click the Verify button. The verification should show a number of log entries which have already been accepted by the Log Server from the specified IP address.
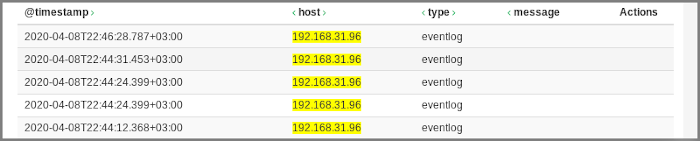
To observe the collected entries, go to the Reports page and click the required IP address (hostname) in the table.

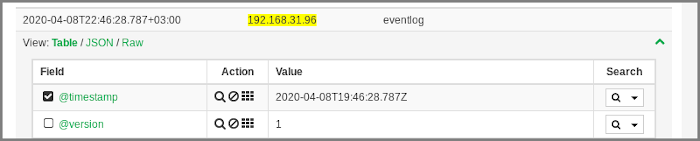
The table with log entries will open. To expand information about the specified entry, click its line in the table.
Each entry contains structured information about its fields and values.